Blastocoel
| Blastocoel | |
|---|---|
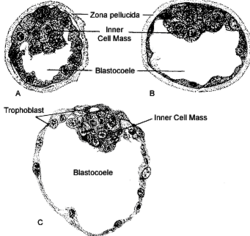 Mammalian blastocoel | |
 Schematic diagram showing the blastocyst, with its embryoblast (inner cell mass) and its trophoblast layer, alongside the surface of the endometrium. | |
| Details | |
| Carnegie stage | 3 |
| Days | 5 |
| Precursor | Morula |
| Gives rise to | Gastrula, primitive yolk sac |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The blastocoel (/ˈblæstəˌsiːl/), also spelled blastocoele and blastocele, and also called cleavage cavity, or segmentation cavity[1] is a fluid-filled or yolk-filled cavity that forms in the blastula during very early embryonic development. At this stage in mammals the blastula is called the blastocyst, which consists of an outer epithelium, the trophectoderm, enveloping the inner cell mass and the blastocoel .
It develops following cleavage of the zygote after fertilization.[2][3] It is the first fluid-filled cavity or lumen formed as the embryo enlarges,[4] and is the essential precursor for the differentiated gastrula.[5][page needed] In the Xenopus a very small cavity has been described in the two-cell stage of development.[6]
In mammals
[edit]After fertilization, the zygote undergoes several rounds of cleavage divisions forming daughter cells known as blastomeres. At the 8- or 16-cell stage, the embryo undergoes compaction and forms the morula. Eventually, the morula is a solid ball of cells that has a small group of internal cells surrounded by a larger group of external cells. Then blastomeres undergo cellular differentiation with internal cells adopting the inner cell mass fate and the external layer becoming trophectoderm. The inner cell mass will go on to become the actual embryo. The external, surrounding cells develop into trophoblast cells, which only contribute to extra-embryonic tissues. At this stage there is no lumen within the embryo. In a process called cavitation, trophectoderm cells transport fluid into the embryo to create a blastocoel, the fluid-filled lumen. The membranes of the trophectoderm cells contain sodium (Na+) pumps, Na+/K+- ATPase and Na+/H+ exchangers, that pump sodium into the embryo. The oviduct cells stimulate these trophoblast sodium pumps as the fertilized egg travels down the fallopian tube towards the uterus.[7] The accumulation of sodium pulls in water through osmosis.[2] The accumulation of water breaks open cell-cell contacts via hydraulic fracturing.[8] To form a single lumen, the fluid from multiple water pockets collects into a single entity in process akin to Ostwald ripening.[8] The blastocoel further expands and the inner cell mass becomes positioned on one side of the trophoblast cells forming a mammalian blastula, called a blastocyst. The axis formed by the inner cell mass and the blastocoel is the first axis of symmetry of mammalian embryo and determines its attachment point to the uterus.
In amphibians
[edit]An amphibian embryo in the 128- cell stage is considered a blastula as the blastocoel in the embryo becomes apparent during this stage. The fluid-filled cavity forms in the animal hemisphere of the frog. However, the early formation of the blastocoel has been traced back to the very first cleavage furrow. It was demonstrated in the frog embryo that the first cleavage furrow widens in the animal hemisphere creating a small intercellular cavity that is sealed off via tight junctions.[3] As cleavage continues, the cavity expands to become the developed blastocoel. The blastocoel is a crucial component of amphibian embryo development. It permits cell migration during gastrulation and prevents the cells beneath the blastocoel from interacting prematurely with the cells above the blastocoel. For instance, the blastocoel prevents the vegetal cells destined to become endoderm from coming in contact with those cells in the ectoderm fated to give rise to the skin and nerves.[9]
Damage to blastocoel
[edit]The blastocoel can be damaged and abolished if the adhesion between blastomeres, provided by cell adhesion molecules like EP-cadherin, is destroyed as mRNA by oligonucleotides. If the mRNA is destroyed, then there’s no EP-cadherin, little to no blastomere adhesion and the blastocoel is non-existent.[4] During the next stage of embryonic development, amphibian gastrulation, the blastocoel is displaced by the formation of the archenteron, during mid-gastrulation. At the end of gastrulation, the blastocoel has been obliterated.[10]
In sea urchins
[edit]At the 120- cell stage, the sea urchin embryo is considered a blastula because of its developed blastocoel, which every embryonic cell surrounds and touches. Every cell is in contact with the proteinaceous fluid of the blastocoel on the inside and touches the hyaline layer on the outside. The loosely connected blastomeres are now tightly connected because of tight junctions that create a seamless epithelium that completely encircles the blastocoel.[11] Even as the blastomeres continue to divide, the blastula remains one-cell thick and thins out as the embryo expands outward. This is accomplished in part due to the influx of water that expands the blastocoel and pushes the cells surrounding it outwards. At this point, the cells have become specified and are ciliated on the opposite side of the blastocoel. The vegetal plate and animal hemisphere develop and secrete a hatching enzyme that digests the fertilization envelope and allows the embryo to now become a free-swimming hatched blastula.[12]
Development of primary mesenchyme
[edit]Important to the sea urchin blastula is the ingression of the primary mesenchyme. After the blastula hatches from the fertilization envelope, the vegetal side of the blastula begins to flatten and thicken as a small cluster of these cells develop long, thin processes called filopodia. These cells then dissociate and ingress into the blastocoel and are called the primary mesenchyme. The cells move randomly along the inside of the blastocoel, until they become localized in the ventrolateral region of the blastocoel.[12][11]
In birds
[edit]Similar to mammals, fertilization of the avian ovum occurs in the oviduct. From there the blastodisc, a small cluster of cells in the animal pole of the egg, then undergoes discoidal meroblastic cleavage. The blastoderm develops into the epiblast and hypoblast and it is between these layers that the blastocoel will form. The shape and formation of the avian blastodisc differs from amphibian, fish, and echinoderm blastulas, but the overall spatial relationship of the blastocoel remains the same.[5][page needed]
Formation of primitive streak
[edit]The avian blastocoel is important during the development of the primitive streak. The ingression of the endodermal precursor cells form the epiblast into the blastocoel and the migration of lateral cells of the posterior epiblast towards the center form the early primitive streak. As these cells converge inward, a depression forms called the primitive groove and functions as an opening through which cells travel into the blastocoel. As cells migrate into the blastocoel, they undergo an epithelial-to-mesenchymal transformation.[5][page needed]
In zebrafish
[edit]Unlike amphibian, echinoderm, mammalian, and avian embryos, zebrafish do not have a defined blastocoel. Rather, they have small, irregular extracellular spaces that are formed between the cells of the blastodisc sitting atop the yolk.[13]
References
[edit]- ^ "Definition of BLASTOCOEL". Merriam-Webster.
- ^ a b Biggers, JD; Borland, RM; Powers, RD (1977). "Transport Mechanisms in the Preimplantation Mammalian Embryo". Ciba Foundation Symposium 52 - the Freezing of Mammalian Embryos. Novartis Foundation Symposia. Vol. 52. pp. 129–53. doi:10.1002/9780470720332.ch7. ISBN 9780470720332. PMID 145938.
{{cite book}}:|journal=ignored (help) - ^ a b Kalt, Marvin R. (1971). "The relationship between cleavage and blastocoel formation in Xenopus laevis. I. Light microscopic observations". Journal of Embryology and Experimental Morphology. 26 (1): 37–49. PMID 5565077.
- ^ a b Heasman, Janet; Crawford, Aaron; Goldstone, Kim; Garner-Hamrick, Peggy; Gumbiner, Barry; McCrea, Pierre; Kintner, Chris; Noro, Chikako Yoshida; Wylie, Chris (1994). "Overexpression of cadherins and underexpression of β-catenin inhibit dorsal mesoderm induction in early Xenopus embryos". Cell. 79 (5): 791–803. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(94)90069-8. PMID 7528101. S2CID 33403560.
- ^ a b c Gilbert, Scott F. (2010). Developmental biology (9th ed.). Sunderland, Mass.: Sinauer Associates. ISBN 978-0-87893-384-6.
- ^ Wolpert, Lewis (2015). Principles of development (Fifth ed.). Oxford, United Kingdom. p. 375. ISBN 9780199678143.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ Wiley, Lynn M. (1984). "Cavitation in the mouse preimplantation embryo: and the origin of nascent blastocoele fluid". Developmental Biology. 105 (2): 330–42. doi:10.1016/0012-1606(84)90290-2. PMID 6090240.
- ^ a b Dumortier, Julien G.; Le Verge-Serandour, Mathieu; Tortorelli, Anna Francesca; Mielke, Annette; De Plater, Ludmilla; Turlier, Hervé; Maître, Jean-Léon (2019). "Hydraulic fracturing and active coarsening position the lumen of the mouse blastocyst". Science. 365 (6452): 465–468. doi:10.1126/science.aaw7709.
- ^ Nieuwkoop, PD (1973). "The organization center of the amphibian embryo: its origin, spatial organization, and morphogenetic action". Advances in Morphogenesis. 10: 1–39. doi:10.1016/b978-0-12-028610-2.50005-8. ISBN 9780120286102. PMID 4581327.
- ^ Purcell, SM; Keller, R (January 1993). "A different type of amphibian mesoderm morphogenesis in Ceratophrys ornata". Development. 117 (1): 307–17. doi:10.1242/dev.117.1.307. PMID 8223254.
- ^ a b Galileo, Deni S.; Morrill, John B. (1985). "Patterns of cells and extracellular material of the sea urchinLytechinus variegatus (Echinodermata; Echinoidea) embryo, from hatched blastula to late gastrula". Journal of Morphology. 185 (3): 387–402. doi:10.1002/jmor.1051850310. PMID 29991195. S2CID 51615081.
- ^ a b Cherr, GN; Summers, RG; Baldwin, JD; Morrill, JB (15 June 1992). "Preservation and visualization of the sea urchin embryo blastocoelic extracellular matrix". Microscopy Research and Technique. 22 (1): 11–22. doi:10.1002/jemt.1070220104. PMID 1617206. S2CID 32044141.
- ^ Kimmel, Charles B.; Ballard, William W.; Kimmel, Seth R.; Ullmann, Bonnie; Schilling, Thomas F. (1995). "Stages of embryonic development of the zebrafish". Developmental Dynamics. 203 (3): 253–310. doi:10.1002/aja.1002030302. PMID 8589427. S2CID 19327966.
Further reading
[edit]- Dorlands Staff (2004). "blastocoel [distionary entry]". Dorland's Illustrated Medical Dictionary (online). Amsterdam, NDE: Elsevier-Saunders. Retrieved 30 January 2016. "blastocoel...[blaso- + -coele] the fluid-filled cavity of the mass of cells (blastula) produced by cleavage of fertilized ovum. Sometimes spelled...[c]alled...'Also' blastocoelic ...pertaining to the blastocoele."; Dorlands.com
- Gilbert, Scott F (2000). "Early Mammalian Development". Developmental Biology (6th ed.). Sunderland: Sinauer Associates. ISBN 0-87893-243-7.
- Gilbert, Scott F (2000). "Early Amphibian Development". Developmental Biology (6th ed.). Sunderland: Sinauer Associates. ISBN 0-87893-243-7.
- Gilbert, Scott F (2000). "The Early Development of Sea Urchins". Developmental Biology (6th ed.). Sunderland: Sinauer Associates. ISBN 0-87893-243-7.
